2175: Shortest Path with Obstacle(1547A)
Description
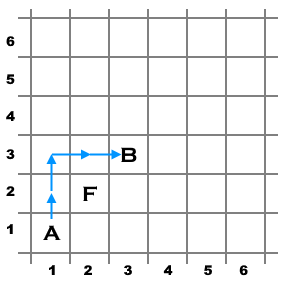
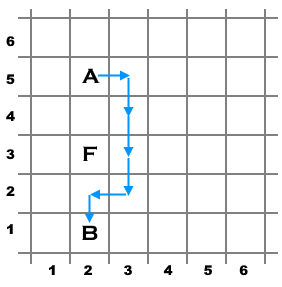
There are three cells on an infinite 2-dimensional grid, labeled AA, BB, and FF. Find the length of the shortest path from AA to BB if:
- in one move you can go to any of the four adjacent cells sharing a side;
- visiting the cell FF is forbidden (it is an obstacle).
The first line contains an integer tt (1≤t≤1041≤t≤104) — the number of test cases in the input. Then tt test cases follow. Before each test case, there is an empty line.
Each test case contains three lines. The first one contains two integers xA,yAxA,yA (1≤xA,yA≤10001≤xA,yA≤1000) — coordinates of the start cell AA. The second one contains two integers xB,yBxB,yB (1≤xB,yB≤10001≤xB,yB≤1000) — coordinates of the finish cell BB. The third one contains two integers xF,yFxF,yF (1≤xF,yF≤10001≤xF,yF≤1000) — coordinates of the forbidden cell FF. All cells are distinct.
Coordinate xx corresponds to the column number and coordinate yy corresponds to the row number (see the pictures below).
Output tt lines. The ii-th line should contain the answer for the ii-th test case: the length of the shortest path from the cell AA to the cell BB if the cell FF is not allowed to be visited.
Sample Input Copy
7
1 1
3 3
2 2
2 5
2 1
2 3
1000 42
1000 1
1000 1000
1 10
3 10
2 10
3 8
7 8
3 7
2 1
4 1
1 1
1 344
1 10
1 1
Sample Output Copy
4
6
41
4
4
2
334